DBMS Architecture Explained | Three-Schema Architecture & Database Design Patterns
Database Management Systems (DBMS) are built to abstract data complexities and provide users a simplified and secure interaction layer. This tutorial explains how data is viewed at various abstraction levels, the role of schemas and instances, database languages, data models, and application interaction mechanisms. It also covers the role of a Database Administrator (DBA) and common DBMS architectures used in real-world applications.
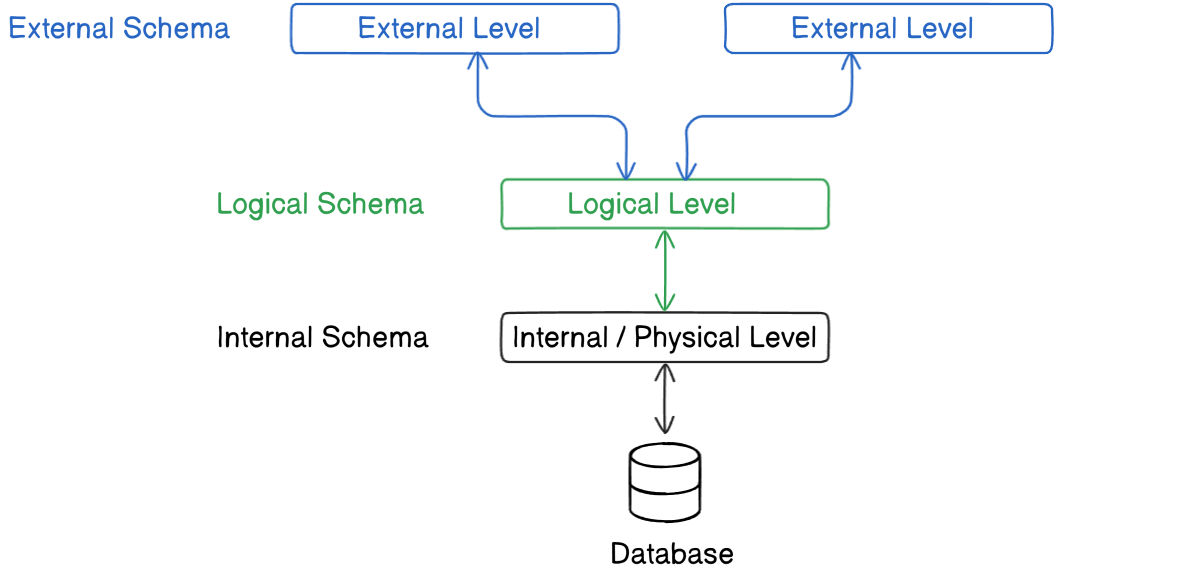
View of Data (3-Schema Architecture)
Section titled “View of Data (3-Schema Architecture)”Purpose:
Section titled “Purpose:”- Provides abstraction between data storage and user interaction.
- Allows multiple users to access the same data with personalized views.

Levels of Abstraction:
Section titled “Levels of Abstraction:”1. Physical Level / Internal Level
Section titled “1. Physical Level / Internal Level”- Describes how data is actually stored, in forms of bits/bytes, in which file format.
- Uses low-level structures like N-ary trees, compression, or encryption.
- Defines the physical schema.
- Goal: Enable efficient access to data via optimized storage strategies.
2. Logical Level / Conceptual Level
Section titled “2. Logical Level / Conceptual Level”- Describes what data is stored and the relationships among data.
- Used by DBAs to define the logical schema.
- Users at this level do not require knowledge of physical storage.
- In General, when we say DB schema it refers to Logical Schema.
- Goal: Focus on ease of use and application design.
3. View Level / External Level
Section titled “3. View Level / External Level”- Highest level of abstraction; provides different views to different users.
- Defines subschemas relevant to specific user groups.
- Enhances security by hiding sensitive parts of the database.
Instances and Schemas
Section titled “Instances and Schemas”| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
Instance | Data stored in the database at a specific moment |
Schema | Structural design or blueprint of the database |
Types | Physical schema, Logical schema, View schema (subschemas) |
- Schema defines the data structure and changes infrequently.
- Instances reflect the current data and change frequently.
- Logical schema is critical for application development.
- Physical data independence ensures schema changes don’t affect applications.
Data Models
Section titled “Data Models”Definition:
Section titled “Definition:”A data model is a collection of conceptual tools for describing:
- Data
- Relationships
- Semantics
- Constraints
Examples:
Section titled “Examples:”- Entity-Relationship (ER) Model
- Relational Model
- Object-Oriented Model
- Object-Relational Model
These are used to design databases at the logical level.
Database Languages
Section titled “Database Languages”| Language | Purpose | Examples / Notes |
|---|---|---|
DDL | Define schema & structure | CREATE TABLE, ALTER, DROP |
DML | Query & manipulate data | INSERT, SELECT, DELETE, UPDATE |
- In practice, most systems use a unified language like SQL for both
DDLandDML. - Query language is a subset of DML for data retrieval.
Example: DML Operations
Section titled “Example: DML Operations”SELECT * FROM Students;INSERT INTO Students VALUES (1, 'Akash', 'CSE');UPDATE Students SET name = 'A. Halder' WHERE id = 1;DELETE FROM Students WHERE id = 1;Accessing Database from Application Programs
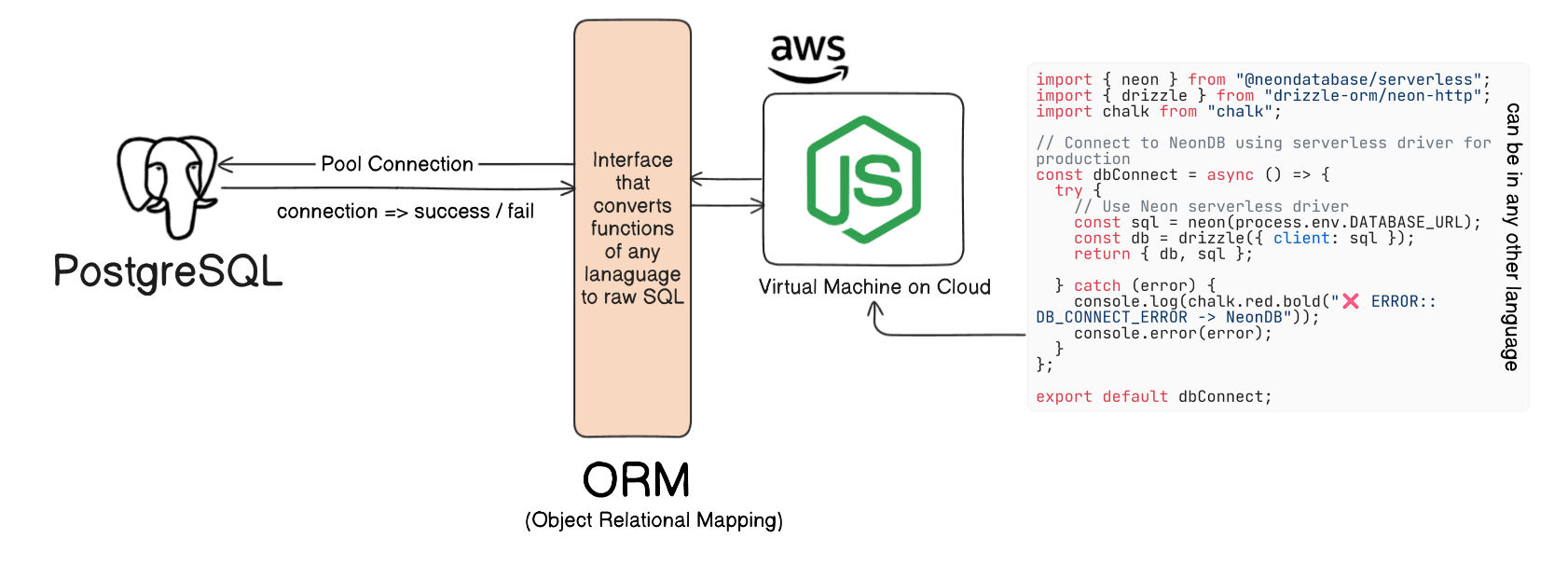
Section titled “Accessing Database from Application Programs”How It Works:
Section titled “How It Works:”- Applications written in languages like PHP, C++, Java, JavaScript, TypeScript send queries to the DB.
- These use APIs to send DDL/DML statements and retrieve results.
Common APIs:
Section titled “Common APIs:”| API | Platform | Language |
|---|---|---|
ODBC | Microsoft | C/C++ |
JDBC | Java-based | Java |
Drizzle/Prisma | JavaScript / TypeScript based | JavaScript / TypeScript |
Example:
Section titled “Example:”- Amazon may store its customer data in any-language and can use an ORM to fecth it from the DB
- A blog System like https://akashhalder.in/blogs/explore is getting powered by this type of interface(ORM)
Database Administrator (DBA)
Section titled “Database Administrator (DBA)”The DBA manages and controls access to both data and DBMS operations.
Functions:
Section titled “Functions:”-
Schema Definition
-
Storage & Access Method Selection
-
Modifying Schema & Physical Organization
-
Authorization Management
-
Routine Maintenance
- Backups
- Security patching
- Software upgrades
DBMS Application Architectures
Section titled “DBMS Application Architectures”T1 Architecture – Single-Tier
Section titled “T1 Architecture – Single-Tier”- DBMS, application, and client reside on the same machine.

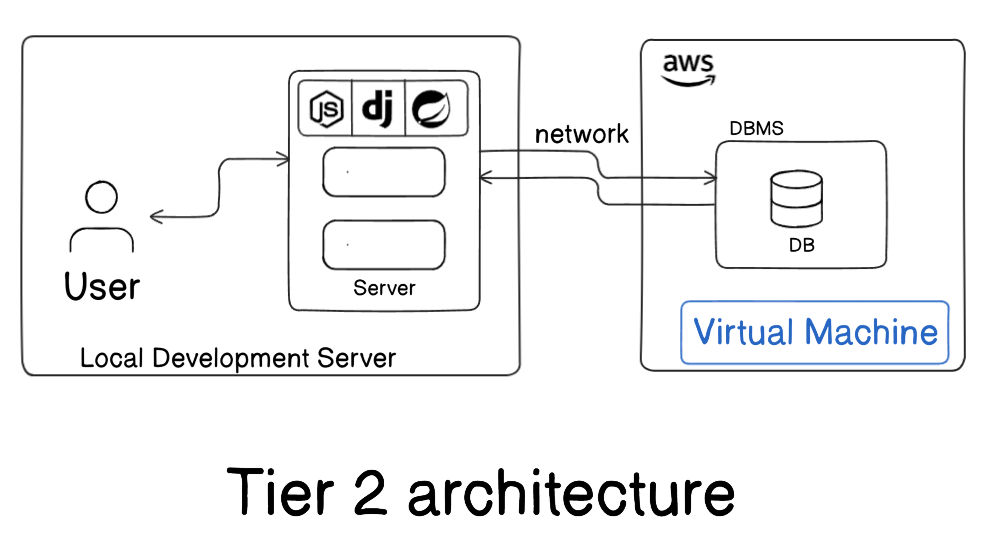
T2 Architecture – Two-Tier
Section titled “T2 Architecture – Two-Tier”- Client sends queries to the DB server using APIs.
- Business logic may reside partly on the client.
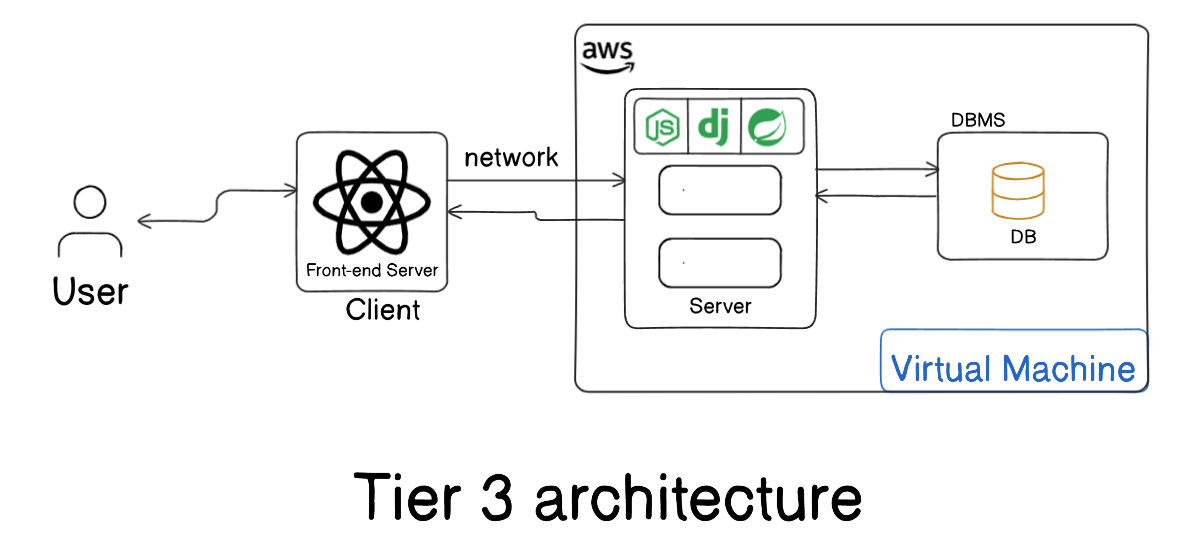
T3 Architecture – Three-Tier (Used in Web Apps)
Section titled “T3 Architecture – Three-Tier (Used in Web Apps)”- Client → App Server → DB Server
- App server handles business logic and prevents direct DB access.
- Improves security, scalability, and data integrity.
Advantages of T3
Section titled “Advantages of T3”| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Scalability | Supports distributed application servers |
| Data Integrity | App server ensures consistent transaction logic |
| Security | Clients have no direct access to DB → safer |